Supporting the TCFD recommendations
The Seven Bank Group has set to “contribute to the prosperity of our society and the future of the Earth” as one of its five material issues, and considers responses to climate change to be one of its most important management issues. The Seven Bank Group expressed an endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) in 2021. In 2023, we conducted a scenario analysis to measure the impact of climate change on our business activities and revenues in the ATM platform business, which is our core business, which identified risks and opportunities from climate change and estimated the financial impact. Responding to the potential impact of climate change risks and opportunities and taking specific measures, the entire Group will take various initiatives aimed at realizing a decarbonized society.
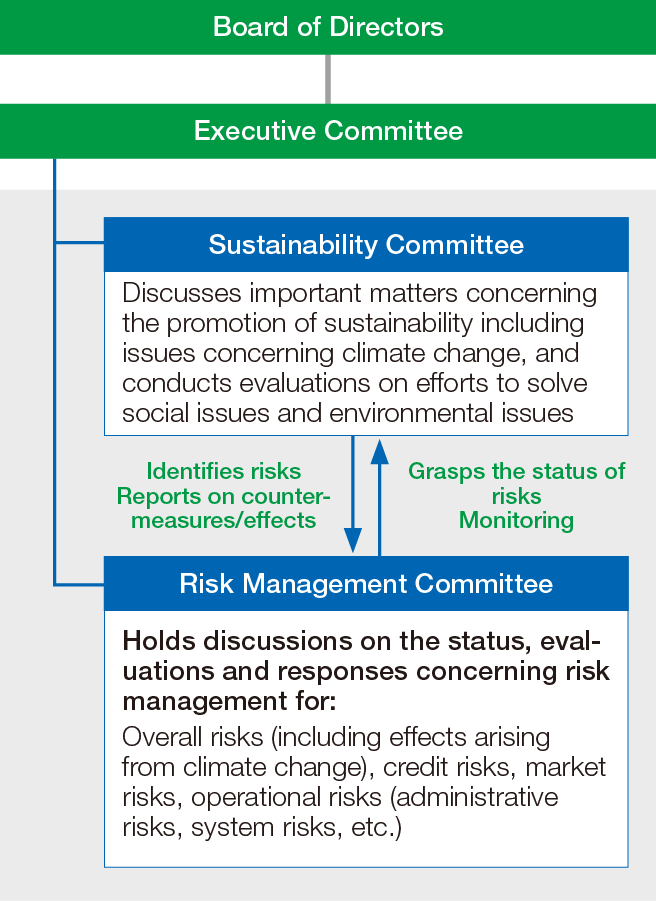
Governance
In the Seven Bank Group, important matters related to climate change are discussed in the Sustainability Committee, which is an advisory body to the Executive Committee. We disclose such sustainability information for the entire group, including the progress of initiatives addressing social and environment issues conducted by each group companies and prepare for external evaluation.
With regard to climate-related risks, we assess the status of overall risk management including impacts arising from climate change and take action in cooperation with the Risk Management Committee, which is an advisory body to the Executive Committee in accordance with the “Basic Policy on Risk Control” established every fiscal year by the Board of Directors, to quarterly check the overall risk status. We have established a system to ensure that, by the Sustainability Committee and the Risk Management Committee, matters concerning sustainability including climate change are referred to and reported to the Executive Committee and the Board of Directors, which makes decisions on basic sustainability policies and important matters in business operations and oversee business execution as a body responsible for management decisions and oversight.
Strategy
The Sustainability Committee conducted a scenario analysis for the year 2030, based on information as of the end of March 2022 targeting our core ATM platform business. In the analysis, the financial impact due to the physical risk of extreme weather was estimated, which is assumed to have a significant business impact.
Analysis process

Conditions of assumed scenarios
The scenario analysis of climate change was conducted assuming the 2 degree limit scenario and the 4 degree scenario based on reports issued by International Energy Agency (IEA) and Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). We identified a wide variety of potential factors impacting our ATM services under each of scenario, assessed the financial impact, and then identified risks and opportunities.
Assumption of scenario analysis
| Items | The 2 degree limit scenario | The 4 degree scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Reference scenarios | (2 degree scenario)IEA Sustainable Development Scenario, IPCC RCP2.6 (1.5 degree scenario)IEA Net Zero Emissions by 2050 | (4 degree scenario)IEA Stated Policies Scenario,IPCC RCP8.5 |
| Target year | As of 2030 | |
| Worldview | The scenario assumes an average temperature increase of less than 1.5°C above the pre-industrial level by 2100. Policies, laws, and regulations will be more stringent than now to achieve carbon neutrality to control problems from climate change. | The scenario assumes an average temperature increase of 3.2°C to 5.4°C (about 4°C) above the pre-industrial level by 2100. No proactive policies, laws, or regulations are put in place to mitigate problems from climate change, while extreme weather events intensify remarkably. |
Identified climate change risks and opportunities
| Type of risk/opportunity | Assessment item | Projected time-frame | Business impact | Financial impact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4℃ | 1.5℃ | |||||
| Transiti- on risk |
Policy and regulations | Regulations on resource recycling | Medium- to long-term |
● Regulations on the distribution and use of fossil fuel-derived plastics used in ATMs will require shift to alternative materials such as bioplastics ● A shift to recyclable materials and structures will be required, increasing costs for adaptation |
− | Medium |
| Change in market | Change in raw material costs | Medium- to long-term | ● Increase in the prices of fossil fuel-derived plastics used in ATMs due to higher crude oil prices can increase manufacturing costs | − | Medium | |
| Change in energy costs | Medium- to long-term |
● Increased demand for renewable energy can bring up electricity prices and increase operating costs for offices and data centers
● Higher gasoline prices will increase costs such as guarded transportation costs |
− | Small | ||
| Physical risk | Acute | Frequent and intensified extreme weather events | Short- to long-term |
● ATM failures due to flooding, transportation networks disruption due to natural disasters, decrease of transactions due to shutdowns of business operators with ATMs installed, decrease of profitability of our core business ATM services
● The number of ATM transactions decreases as people go out less, resulting in lower income |
Large | Medium |
| Chronic | Rise in average temperature | Short- to long-term | ● Air-conditioning costs for offices and eastern and western data centers will increase | Medium | Small | |
| Opportu- nity |
Product and services | Growing environmental awareness | Medium- to long-term |
● Demand for replacement to Seven Bank ATMs will increase due to replacement of ATMs to those with advanced energy-saving functionality and due to an increasing interest in recyclable ATMs ● Demand for ATMs as sustainable social infrastructure will increase as the initiatives addressing climate change progress across the ATM network as a whole |
Medium | Small |
| Market | Need for cash in ordinary times/emergency situations | Short- to long-term |
● Rising temperatures will increase the number of customers visiting convenience stores and increase opportunities to use ATMs ● Demand for mobile ATM vehicle dispatch services as disaster response measures will increase ● Increased need for cash in the event of a disaster will increase the number of transactions |
Medium | Small | |
*Short-term: 1 year, Medium-term: 1 to 5 years, Long-term: 5 to 30 years
Calculation of financial impact
In addition, for the damage and impact of extreme weather events on our ATMs, which were evaluated as having a large business impact as a result of the scenario analysis, we estimated the frequency and probability of floods and storm surges occurring in the areas where our ATM locations nationwide using hazard maps and calculated damage to the actual ATM machines, including ATM recovery cost and financial loss due to ATM shutdowns, and estimated the financial impact.
| Assumptions | Calculation | Calculation result (in millions of yen/year) |
|---|---|---|
| In both the 4 degree scenario and the 2 degree limit scenario, as of 2030, physical damage from floods and storm surges increases due to intensified severe extreme weather events. We have a large number of ATMs nationwide and expect to have a significant financial impact from the increasing frequency of floods and storm surges. | The following items are estimated based on the Manual for Economic Evaluation of Flood Control Investment (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) and other references. ● Damage to ATM asset due to flooding ● ATM recovery cost ● Losses due to ATM shutdown
|
805~1,408 |
Seven Bank’s major initiatives
Responding to the potential impact of climate change risks and opportunities, the Seven Bank Group has been taking various actions to enable a decarbonized society.
Risk
| Risk type | Assessment item | Major initiatives | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transiti- on risk |
Policy and regulations | Regulations on resource recycling |
Response for existing ATMs
● For ATMs, we have proactively introduced recycled materials and adopted an easy-to-maintain structure, etc. from the design phase. In the event of defects, we perform parts replacement and maintenance and make other efforts to extend its life.
● ATMs removed and collected due to renovation and closure of Seven-Eleven stores and replacement with fourth-generation ATMs are, if they are reusable machines, reused after maintenance, or reused as parts. ● Old unrecyclable ATMs are recycled as resources through recycling business operators. Thus, we achieve a recycling rate of around 100% for ATMs
Response for next-generation ATMs
● We proactively engage in collaboration with academia, etc. in view of exploration of new materials and research and development of recyclable materials for discussion of next-generation ATMs.
|
| Change in market | Change in raw material costs | ||
| Change in energy costs |
● To maintain an appropriate level of cash stored in ATMs, the usage patterns of each individual ATM are currently analyzed using AI technology and the timing of funds needing to be replenished is forecasted. Based on the information, optimal cash transportation routes and the frequency are determined in cooperation with a guarded money transport company. This enables efficient operation considering transportation-related energy consumption and CO2 emissions. ● Starting in 2022 with a data center which is powered by electricity solely from renewable sources, as well as a cloud storage service based on sustainable concerns, we are addressing future changes in energy costs, aiming to achieve complete zero emissions of CO2 by 2025. |
||
| Physical risk | Acute | Frequent and intensified extreme weather events |
● Although we established a structure to ensure business continuity traditionally by having our system bases in eastern and western Japan, in 2021, most core systems were transferred to cloud storage. In cooperation with our business partners, we continue to duplicate our systems and operate them alternately from our sites in eastern Japan and western Japan. At the same time, we have also stepped-up measures for early recovery in the event of failure, which includes rapid fault isolation and enhancing the remote maintenance environment. ● We take measures against blackouts due to disaster by installing an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) on the ATM itself. ● To minimize damage caused by natural disasters, we have established a system with Seven-Eleven to cooperate with the store management teams in the disaster area in advance and utilize the store information sharing system “7VIEW” to grasp the situation in real time and take early action. |
| Chronic | Rise in average temperature | ● Promoting casual office attire and reducing power consumption by heating and cooling equipment | |
Opportunity
| Type | Assessment item | Major initiatives | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Opportu- nity |
Product and services | Growing environmental awareness | ● By March 2025, we have replaced all of our ATM installations with the fourth-generation ATMs, which was first introduced in 2019. Since the initial stage of development, the fourth-generation ATM model aimed to not only improve features and performance but also to contribute even better to society and the environment so as to meet broader customers’ and social needs. We successfully reduced power consumption by 40% compared to the third-generation ATM model in cooperation with our business partners through reconsideration of ATM circuit design and thorough selection of low power consumption parts. Although the total number of ATMs installed increased by 3,598 from the end of March 2019, when the third generation ATMs were in place, total CO2 emissions from all ATMs decreased by 28.1%, leading to a reduction in environmental impact. |
| Market | Need for cash in ordinary times/emergency situations |
● Assuming an increase of ATM replacements by financial institutions to minimize damages to bank branches and ATMs due to natural disasters, we strive for enhancing ATM services as a social infrastructure. ● In the event of a large-scale disaster that disables ATM operations over a wide area, we will dispatch mobile ATM vehicles to help the affected communities through the provision of settlement infrastructure. |
|
Risk Management
The Seven Bank Group incorporated climate change risks into the company-wide risk management system as part of the process of identifying and managing climate-related risks, as the section on the overall risk management policy in the “Basic Policy on Risk Control” requires the Bank to practice agile risk management by responding immediately to changes in the external and internal environment based on risk assessment results and monitoring.
Meanwhile, with regard to opportunities, the Sustainability Committee holds regular hearings on the status of efforts in each business unit to “contribute to the prosperity of our society and the future of the Earth,” which is one of the priority issues, and is strengthening group-wide environmental initiatives. In February 2024, we launched the ATM Partner Sustainability Conference with three major ATM-related business partners. Aiming to build an ATM network that can contribute to solving social and environmental issues more than before, we will continue to drive forward our sustainability strategy as one team including the whole supply chain.
Indicators and Target
In order to measure the environmental impact quantitatively, the Group calculates CO2 emissions for each fiscal year.
In the past, we calculated CO2 emissions for Seven Bank alone, but we have expanded the scope of calculation in Scope 2 starting from this fiscal year. Accordingly, CO2 emissions from the Seven Bank Group on a consolidated basis were calculated for the most recent three fiscal years (from FY2022 to FY2024).
In Scope1, the amount of mobile combustion associated with the use of company vehicles was calculated on a non-consolidated basis for Seven Bank. Although our four overseas subsidiaries also use company vehicles, the consolidated figure is not calculated because numerical records necessary for such calculation are currently hardly available and the impact is deemed to be insignificant due to the limited the number of vehicles subject to calculation. In the future, we plan to consider setting targets for CO2 emissions for the Seven Bank Group in conjunction with the calculation of CO2 emissions in Scope 3 on a consolidated basis.
The scope of calculation for Scope 2 is as follows.
| Japan | Overseas |
|---|---|
|
● Seven Bank, Ltd. Five offices: two in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo and one in Sumida-ku, Tokyo, Yokohama City, Kanagawa Prefecture, Toyonaka City, Osaka Prefecture respectively Three directly-managed Seven Bank ATMs locations: Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo※1, Minato-ku, Tokyo, Osaka City, Osaka Prefecture ● Seven Payment Service, Ltd. One office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo※2 ● ACSiON, Ltd. One office: Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo※2 ● Bank Business Factory Co., Ltd. Three offices: one in Yokohama City, Kanagawa Prefecture and two in Nagasaki City, Nagasaki Prefecture ● VIVA VIDA MEDICAL LIFE CO., LTD.※3 One office: Yamato City, Kanagawa Prefecture ● Seven Card Service Co., Ltd.※4 Three offices: two in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo※5 and one in Saitama-shi, Saitama Prefecture |
● FCTI, Inc. (Dallas, USA)※6 ● PT. ABADI TAMBAH MULIA INTERNASIONAL (Jakarta, Indonesia) ● Pito AxM Platform, Inc. (Manila, the Philippines) ● ABADI TAMBAH MULIA INTERNASIONAL MALAYSIA SDN. BHD.(currently Reachful Malaysia Sdn. Bhd.) (Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia)※7 |
※1 Closed in January 2024.
※2 Uses the same office in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo as Seven Bank, Ltd.
※3 Became a subsidiary in November 2022 (moved to Yokohama City in May 2025).
※4 Became a subsidiary in July 2023.
※5 Has used the same office as Seven Bank, Ltd. in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo since January 2025. It had used a separate office in Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo until then, and both offices are included in the scope of calculation for the period under review.
※6 Moved to the location in April 2024. Had used an office in Los Angeles until March 2024.
※7 Founded in May 2024.
The calculations are based on the GHG Protocol. We basically use the market-based method (calculations based on contracted electricity menus) for Japan, and the location-based method (calculations based on the average emission intensity for the specific region) for other countries. For some sites for which it is difficult to determine the actual amount of electricity used, the estimated floor area is used under the location-based approach. All calculations are based on Persefoni’s carbon-accounting platform.
Scope 3 emissions of Seven Bank on a non-consolidated basis from FY2021 to FY2023 are as follows.
(t-CO2)
| FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1 | Use of fuel (mobile combustion) ※Non-consolidated figure for Seven Bank | 10 | 11 | 9 |
| Scope2 | Indirect emissions from the use of electricity, heat, etc. supplied by others ※Consolidated figure for Seven Bank Group |
891 | 816 | 816 |
| FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope3 | Categories 1, 5, 6, 7, 12, 13 and other | 17,293 | 17,787 | 17,473 |
Climate initiatives
- Seven Bank’s Sustainability
- Top Message
- Sustainability Management
- ESG
- Environment
- Social
- Corporate Governance
- Materiality
- Materiality top
- Fundamental value
Offer a social infrastructure available anytime with safety and security - Social value
Realize a wide variety of services accessible to anyone, anywhere - Creation of new values
Create unique values beyond our customers’ expectations - Source of value creation
Create a society where everyone can be active - Value creation for the future
Contribute to the prosperity of our society and the future of the Earth
- Social Contribution Activities
- For Future Generations
- Social Contribution Activities
- Other Corporate Information
- Investor Relations
- Company
